Understanding Satellite Payloads: A Comprehensive Guide
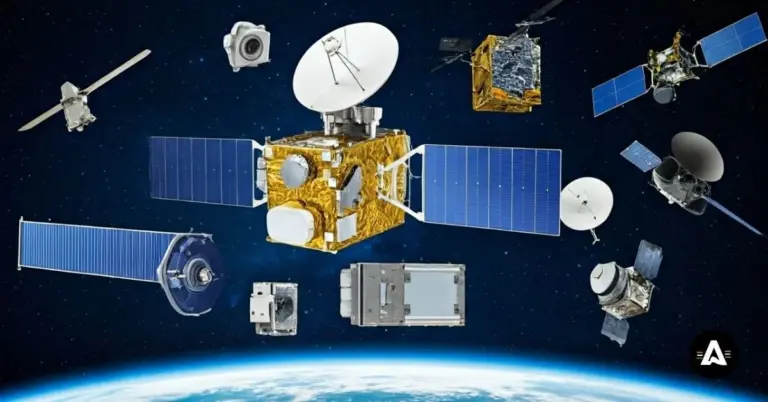

Satellite payloads are the important tools, sensors, and parts that help meet the main mission objectives of each spacecraft. These payloads do many jobs, from checking weather patterns to helping with scientific research.
The payload part and the bus system have different roles. Payloads work on the main job of the mission, while the bus handles the regular work needed to keep the spacecraft running.
The type of satellite payload changes based on the mission. A communication payload is there to send data, while an Earth observation payload helps by taking pictures and watching weather patterns.
A famous payload, like ISRO’s Mars Color Camera, helps provide new information about the Martian atmosphere and shows the surface features of Mars.
Better technology is always changing what payloads can do, helping scientific research and making global data more open and useful to people around the world.
Introduction
Every satellite that goes up into space brings scientific instruments called payloads. These payloads play a crucial role. They help make sure the satellite can get the data it needs to meet its mission objectives. Each payload is built with a lot of care. That way, it can do its job well and send good information back to the spacecraft.
The payloads and the spacecraft work as a team. When you learn how the payloads work, you get to know more about what happens during a space mission. Some payloads check on the weather of Mars, and some of them look at solar radiation. Payloads like these be important when we want to know more about Mars and space. They help people discover new things about the universe.
What Are Satellite Payloads?
Satellite payloads are the main systems on a spacecraft. They are made to help the satellite reach the mission objectives. These payloads can have scientific instruments, sensors, or other tools that are important to the job. The payloads help the satellite get the right data or finish a task. The type of payloads a satellite has will change for each mission. Payloads give every satellite its own special way to work.
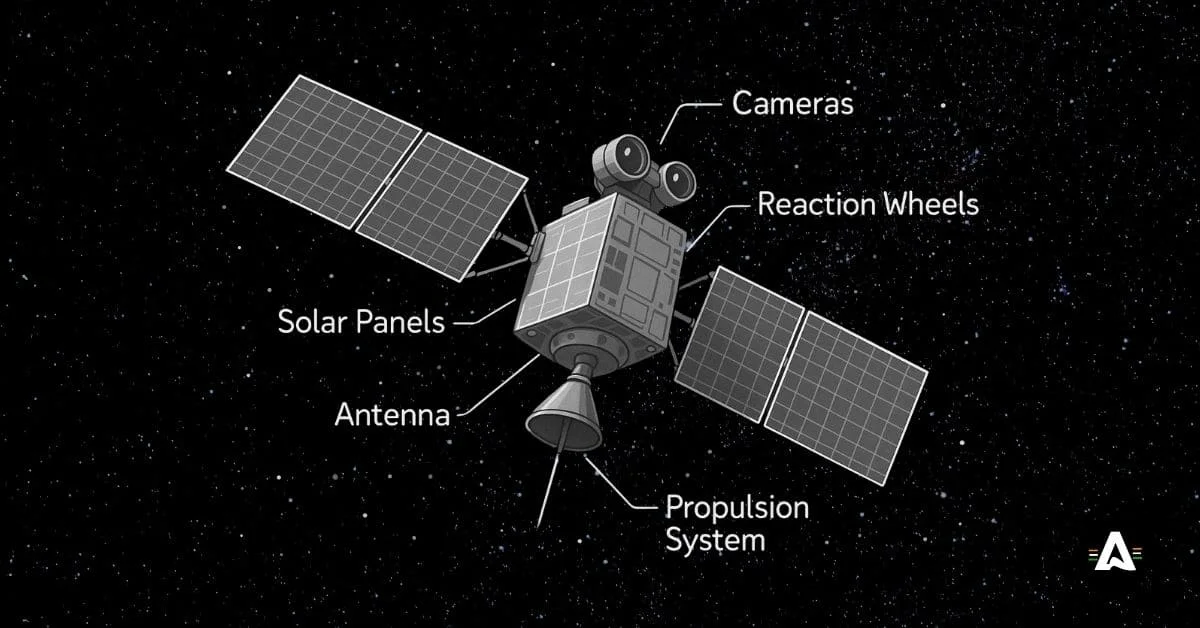
Sensors found in the payloads often check the weather or look at surface features. No matter if the job is to help with worldwide communication or help with scientific research, payloads be what make the satellite work. Payloads use sensors to get the data people need for the mission. Without the payloads, a satellite could not do its job.
Core Functions of a Satellite Payload
Satellite payloads are the parts of a spacecraft that do the main work. These payloads keep getting, handling, or passing on key information that is needed to finish the mission objectives. They have antennas, sensors, and scientific instruments, and these are all set up to help meet the goals of the mission. In these payloads, antennas have a crucial role. The antennas help send data between the spacecraft and the Earth. This makes sure the link is strong and reliable.
Sensors get used to find out about things in the world around us. They also help people take clear pictures. Many payloads for Earth observation use these sensors to look at weather patterns. They can also help keep track of crops in some places. There are some scientific instruments called spectrometers. These look into space to get details about what is in the air. They also watch what is happening in space.
Payloads can be changed to meet different needs. For example, the Mars Orbiter Mission uses a sensor called the Methane Sensor for Mars. This sensor checks the amount of methane concentration on the surface of Mars. Even though every payload works in its own way, they all have one main goal. Payloads are at the center of every satellite mission. So, all the plans and targets make sure the data is useful for people on Earth to take action.
Difference Between Payload and Bus Systems
The payload and the bus system each have a job inside the spacecraft. The payload is the part made for the mission objectives. It holds the special tools like antennas, cameras, and sensors. These help the spacecraft get and send the right data. The bus system is the base for the payload. It gives the power and handles things like heat and movement. This helps guide the spacecraft, making sure all parts work well together.
Payloads are built to do their own specific jobs in space. For instance, NASA uses payloads on satellites to watch solar wind and other things. ISRO’s payloads help study Mars. The bus system helps all these payloads work well together and makes sure the spacecraft can deal with tough space conditions.
In the end, the payloads and the bus system be together as one in the spacecraft. Payloads are there to help reach the mission objectives. The bus system supports them. It keeps all of it working, so every part of the mission can go right. They must work together in the spacecraft to make the mission happen.
Types of Satellite Payloads by Mission
Satellite payloads are made for many different missions. Some payloads help with global data by using antennas and other tools to send it anywhere. This way, the data can reach people around the world without stops.
Earth observation payloads work with sensors. They take pictures of surface features on the earth. This helps us watch weather patterns. It is a way to keep track of changes in the environment too.
Some payloads are made to help with scientific research. They have tools to study things, like the air’s chemistry, solar radiation, or objects in space. All these different payloads show that each one is made with a special job in mind. This helps the satellite do its work well.
Communication Payloads – Enabling Global Connectivity
Communication payloads are a big part of how we all stay connected now. They help global data move smoothly from one place to another. These payloads often carry things like antennas and transponders. They send important information, like TV channels and broadband internet, over long distances. This lets people get and use this information when they want.
Most payloads use UHF, Ku, and Ka bands for their signals. Sometimes, these payloads face problems with signal loss. But they also help make signals stronger so that everything keeps working as it should.
- Transponders in satellites like the GSAT series take signals, make them stronger, and send them to the right place.
- Antennas are important in the way data moves. They help connect ground stations on Earth with satellites up in the sky.
- The Ku and Ka bands are good for fast needs, like live streaming and satellite internet.
You can use payloads in many ways. People use them for work, travel, or fun. These parts help to send global data around the world. They keep all people connected. Payloads make sure that data always gets to where it needs to go. This helps us all stay close in many ways.
Earth Observation and Imaging Payloads – Applications in Weather & Agriculture
Earth observation satellites use payloads that help track weather patterns and look at farms. These payloads have sensors that pick up clear images and important data about the environment. Cameras like synthetic aperture radar and multispectral ones help make very detailed maps.
Payload Type | Functionality |
|---|---|
Weather Monitoring | Capturing atmospheric data and cloud formations |
Surface Imaging | Tracking changes in agricultural zones and waterways |
Environmental Analysis | Observing global environmental shifts |
These payloads are helpful for both governments and researchers. They look at weather, help to stop disasters before they can happen, and help farms make more food. Satellites like EOS-07 carry payloads and sensors that give us important information for solving problems. They use new and advanced technology to help people all over the world.
Scientific and Specialized Payloads
Scientific payloads be built for space science and tests in space. These payloads have many scientific instruments inside, like spectrometers and particle detectors. The instruments help get information about things in space. For example, they gather data on solar radiation and what is in the atmosphere.
Some payloads are made for a special purpose. For example, missions to Mars use photometers. These tools help to measure what is in the Martian atmosphere. This way, the payloads can meet the mission objectives well. All these payloads help us learn more and go further in scientific research.
Navigation, Space Science, and Experimental Payloads
Payloads that help with navigation and space science are very important when we want to learn more about the universe. Navigation payloads use atomic clocks and signal gadgets to show the right time and place. This is how satellite systems such as GPS, Galileo, and NAVIC work.
Space science payloads be tools that help people study solar radiation and how things move in space. These payloads work with spectrometers and magnetometers. They get information about solar wind and coronal mass ejections. With new and better sensors, ISRO’s Aditya-L1 can check the Sun’s magnetic field well.
There are also some experimental payloads that test out new technology. They help us learn about where and when the solar wind moves. Some payloads use robots to gather more data. These payloads make spacecraft better and help people think of new ideas for missions. The flexibility and drive to come up with new things are what set these payloads apart. Thanks to them, there is always something new to learn or make better in this field.
ISRO Payloads for Specific Missions
ISRO’s missions use different payloads that match each science goal. The Mars Orbiter Mission has the Mars Color Camera (MCC). This camera maps surface features and checks what is in the Martian surface. There is also TIS, which looks at how much thermal radiation Mars gives off. The MSM is used to find the methane concentration in the Martian atmosphere.
Another great success from ISRO is the Moon Impact Probe (MIP). This probe used different payloads, like the Altitudinal Composition Explorer (CHANCE). It helped study the lunar surface. New sensors were added to these missions. Those new sensors made the data even better. This lets people and researchers all over the world learn more about many types of planetary environments. The moon impact probe, its payloads, and sensors inside the MIP all played a big role in this.
By using these special payloads, ISRO is able to keep working toward its mission objectives. This work helps us learn more about solar radiation and methane. It also helps us get better images with new and better sensors.
Conclusion
To sum up, satellite payloads are very important parts, and they can change a lot depending on what the mission is meant to do. It is good to know about the differences between payloads that help with talking to each other, watching the Earth, doing science, or other special tasks. When we know this, we see how payloads help people stay connected, keep an eye on the world around us, and help science move forward. The way we build these payloads and what they can do will get better over time. This will help them do more jobs and work better. If you want to know more about payloads, it is smart to stay up-to-date. If you want more ideas or facts about satellite payloads, you can get in touch at any time to learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions
Satellite payloads are important parts of a spacecraft. They carry scientific instruments like antennas and sensors. Sometimes, the payloads have tools like spectrometers too. The main job of payloads is to help the mission reach its goals. This may be collecting data, measuring changes in the air, or sending messages between Earth and the spacecraft in space. Payloads are key to how well the spacecraft works.
Payload choice depends on what the mission is for. If you want to track weather patterns, you need to use sensors made for this job. These sensors go on Earth observation satellites to help gather the needed global data. If the goal is scientific research, you can use new tools and equipment. This helps you test ideas or find out new things. There are also antennas and cameras you can use. They help you collect global data or give information for science. It is very important to pick the right sensors and antennas. This will make your mission work well.
Yes, satellites often take several payloads with them to handle different mission objectives. For example, a satellite can have antennas to help with communication. It may also use sensors to get images, and have scientific instruments for research. By having these payloads, the satellite can work on many things at once. It might take part in Earth studies, research, or space trips in just one mission.
Indian payloads include the Mars Color Camera (MCC). It takes pictures of the surface features on Mars. The Methane Sensor for Mars (MSM) checks for methane in the Martian atmosphere. The Moon Impact Probe also carries other payloads. One of them is called CHACE. It helps study the surface and shows what it is made of at different heights. All of these tools help us learn more about the Moon and Mars.
Better technology helps make payload designs better. This lets there be new sensors, antennas, and scientific instruments for spacecraft. When this happens, the spacecraft work better and can collect more global data. Now, people can use these tools to do harder scientific research in space. For example, they can study the solar wind or watch how the atmosphere moves far out in space.




